Papillomas on the body are a common situation in dermatological practice.The main locations are the armpits, neck, groin, genitals and face.Most neoplasms have a benign course, but the risk of transformation into skin cancer or oncology of any other localization increases under the influence of multiple negative factors.
Why are papillomas dangerous for the human body?
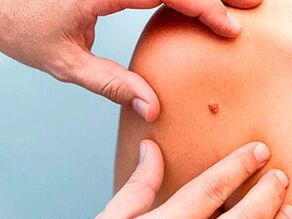
Viral tumors on the body are usually caused by strains with a fairly low oncogenic risk and minimal risk of cellular degeneration.With cellular atypia, rapid growth and changes in the structural characteristics of papillary lesions are observed.
Today, particularly dangerous strains include HPV types 15, 16, 18, 35, 51-59, 66-68.It is interesting that the localization of a cancerous tumor during infection with the human papillomavirus can be absolutely any.
Papillomas on the body appear in the form of warty neoplasms, calluses, flat or genital warts.The dangers and complications caused by HPV generally differ between men and women.
Complications of papillomavirus in men
It is often men who become carriers of infectious strains and transmit them to women through unprotected sexual contact.The main localization of papillomas on the body in men is the genitals, genitals, frenulum and foreskin;papillomas often form in the anus in men.Sometimes growths appear in the armpits and neck.
Symptoms directly depend on location.Clinical manifestations are more typical for the localization of papillomas in the genitals.As a rule, neoplasms are not accompanied by obvious symptoms.
The main complications in men are:
- prostate cancer;
- throat and larynx cancer;
- sexual impotence;
- infertility;
- erectile dysfunction;
- development of adenocarcinoma;
- malignant intestinal tumors.
The transformation of healthy cells into cancerous cells is facilitated by:
- bad habits,
- difficult working conditions,
- frequent stress,
- permanent damage to papillary lesions;
- insufficient hygiene.
Characteristics of dangers in women
In the absence of adequate treatment, HPV in women threatens with even more serious complications due to the peculiarities of the anatomical structure of the genitals and hormonal levels.
The main complications are:
- cervical and appendix cancer;
- dysplasia of the vulva, vaginal vault, cervical canal;
- carcinoma of the uterine structure;
- large genital warts, if a papilloma is diagnosed in the groin in women;
- malignant change in the mucous membranes of the pharynx and genitals;
- genodermatous warts according to the Lewandowski-Lutz pathological type;
- cancer of the esophagus and larynx;
- plantar cancer.
The localization of warts and condyloma in the lumen of the urethral canal leads to disruption of the flow of urine.When localized in the larynx - hoarseness and impaired respiratory function.
Unfortunately, many women perceive any new growth on the skin only from the point of view of aesthetic problems.By removing the papillomas, they hope to have completely solved the HPV problem.When a viral infection is active, the removed tumors reappear and with greater intensity.
It is important to recognize the signs of malignancy of neoplasms in time:
- Changes in shape, size and growth structure;
- Instability of the color of the papillary lesion:
- Painful sensations in the growth area;
- Constant trauma, bleeding, infection.
Regular exposure to negative factors contributes to growth instability and stimulates the transformation of cells into cancer cells.
If papillomas appear, it is recommended to consult a dermatologist to clarify the nature of the pathological rash.
Are papillomas on the body contagious?
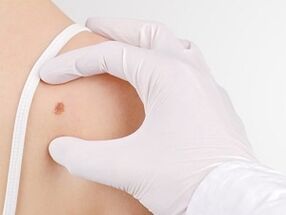
Are papillomas on the body transmitted from person to person?Given the high contagiousness of human papillomavirus infection, patients wonder about the possibility of contracting the virus through contact with foci of viral tumors on the skin.The answer is clear: it is almost impossible to “catch” the virus by touching papillomas.
However, if the skin of the wearer and a healthy person in the contact area is damaged, the risk of infection increases.
There are other ways of transmitting infection:
- sexual contact;
- work activity;
- contact-household route (during a long stay with a virus carrier).
You can also become infected in public places, including public baths, saunas, locker rooms and swimming pools.
There is a concept of autoinfection, when one injured papilloma causes many others over the entire surface of the body.
The penetration of the virus into the human body does not necessarily mean that rashes will appear after a while.With a high immune response of the human body, the volume of antibodies is sufficient to suppress the viral activity of all strains, and against the background of good health, the virus does not appear at all until the end of life.
Of course, even if a person has no symptoms, they still carry a viral infection.
Many papillomas appeared on the body, what does this mean?
The appearance of papillomas on the body in various places characterizes the activation of viral strains.Multiple papillomatous foci signal an increased risk of malignancy.The increased pathogenic activity of viral strains is due to reduced immunity with a persistent progressive course.
The following can cause the body’s immune response to decrease:
- colds;
- hypothermia;
- stressor;
- alcoholism and drug addiction;
- persistent hormonal disorders;
- pregnancy, abortion;
- chronic pathologies of internal organs.
Viral activity can be triggered by simple non-compliance with personal hygiene rules.Somatically, multiple papillomas explain pathologies of internal organs and systems.HPV is often associated with other viral diseases, for example herpes infection.
Papillomas have spread throughout the body: what to do?
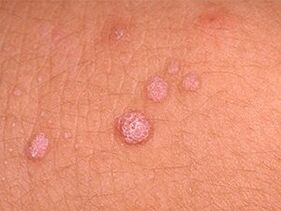
When several papillomas appear, it is important to carry out a differential diagnosis.A professional doctor usually immediately notes the nature of the rash and indicates the possible cause of the tumors.
The main research methods are:
- blood test for antibodies to viruses;
- Digen test to identify strain type, viral structure and oncogenic danger level;
- polymerase chain reaction to detect viral DNA;
- cytological examination of biological material from the cervical canal;
- histological examination of female genital organ samples;
- analysis of warts or condyloma.
A preliminary diagnosis is usually made during the first examination of the patient.Based on the research results and the patient's clinical history, a viral infection is diagnosed or excluded.It is important to distinguish HPV from dermatological diseases, cancer and the herpes virus.
Fight papillomas on the body
Today there is no effective treatment for viral infections, but official medicine is able to create conditions for stable remission and prevention of rashes.The infection itself is not dangerous, but the formation of papillomas increases the risk of cellular malignancy and the appearance of tumors.
Treatment
A promising direction is drug therapy:
- Immunomodulators based on interferons to stimulate the immune system;
- Antiviral agents;
- Vitamins to create strong immunity and restore the body;
- Local preparations to eliminate papillomas.
In case of secondary infection, bacterial therapy and antiseptic treatment are prescribed.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are suitable for relieving pain.
Deletion
Removal of tumors is possible thanks to modern hardware techniques and cosmetic surgery.
There are several effective methods for tumor excision:
- scalpel;
- laser;
- radio wave;
- cryodestruction;
- chemical;
- electrocoagulation.
No operation prevents the further formation of pathological growths.Without adequate antiviral treatment, eliminating external signs only gives temporary results.
HPV is a common infection that can be contracted through sexual contact, as well as regular kissing.The main prevention is to vaccinate a child aged 12 to 14 years before the first sexual experience.It is important to monitor the hygiene of the skin and genitals.Unfortunately, even barrier methods of contraception are not able to guarantee 100% protection against human papillomavirus infection.Rapid patient response to rashes is the key to safe and timely treatment, including preventing the risk of cancerous tumors.























